Demand Forecast
 Demand Forecast
Demand Forecast
Transport Demand Forecast
Transport Forecasts
- Transport demand is a quantitative input to evaluate supply strategy of transport facilities and land use planning.
- Presented as travel volume based on transport system usage, including transport facilities and transport services.
- The derived demand was created by continuous interaction of transport systems and activity systems.
Definition
- Transport demand forecasting is to predict future transport demand when establishing transport plans within a given budget.
- Since transport demand closely interacts with socioeconomic environment and land use, future socioeconomic indexes and land use patterns need to be estimated first.
- The forecast is based on current travel patterns of transport systems and under the assumption that general conditions will not greatly change. Therefore, drastic or detailed changes can result in prediction errors.
Usage
- Transport demand forecasting is used as important basic data to evaluate the efficiency of transport facility supply and transport policy, such as road construction, public transport introduction, and transport demand management implementation.
- It is also used to evaluate land use plans by estimating travel volume according to the change of land use patterns within a given transport system.
Forecast Evaluation
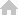
- Compiling data on the network (including transport zone, links, and nodes) and O/D travel volume within the current base year’s land use patterns.
- Conducting the base year’s network (including transport zone, links, and nodes) and O/D travel volume as close as possible to reality.
- Predicting future transport demand on target year zones, links, and nodes) and O/D travel volume within the current base year.
- For the prediction to be correct, the future general conditions need to stay largely the same from the standpoint of travel patterns. Reflecting all long-term changes of passenger patterns is rather limited.
- Accurate prediction on the change of target year conditions need to stay largely the same from the travel pattern in the transport demand forecast.
[ Process of Transport Demand Forecast ]
Forecasting Techniques
Transport demand rough estimation method
- Main models can be a trend extension method and elasticity of demand method.
- Required time and cost is minor for this method, but it only gives a rough prediction with low accuracy.
Trend extension method
- Use of previous year’s data to predict performance-based traffic demand for target year.
- Applying trend lines (linear, exponent, logarithm, multinomial, moving average) of previous transport demand.
Elasticity of demand method
- Using sensitivity of transport demand according to changes of transport systems or facilities.
- Predicting transport demand using elasticity of demand, which is the volume change of transport demand according to the change of transport facility systems.
Sequential transport demand model
- The traditional four-step transport demand model is the typical sequential sequential model. This model predicts transport demand, assuming passengers make decisions through sequential choices.
- This is currently the most common transport demand forecast method. An accurate description is possible by verifying the results of each step.
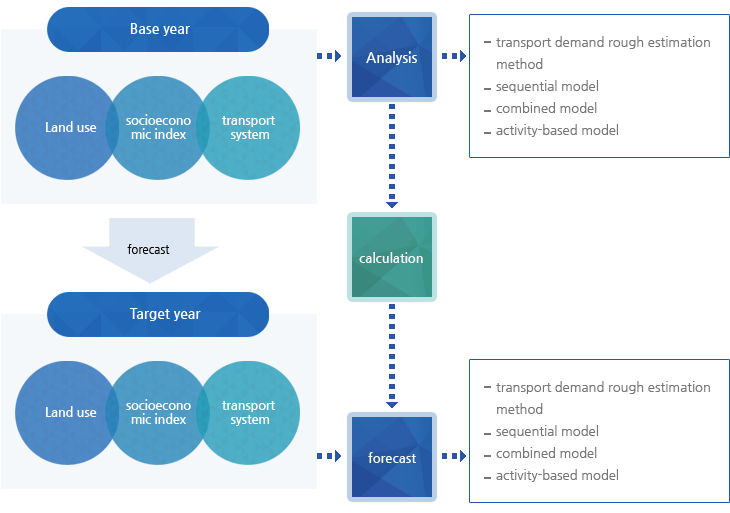
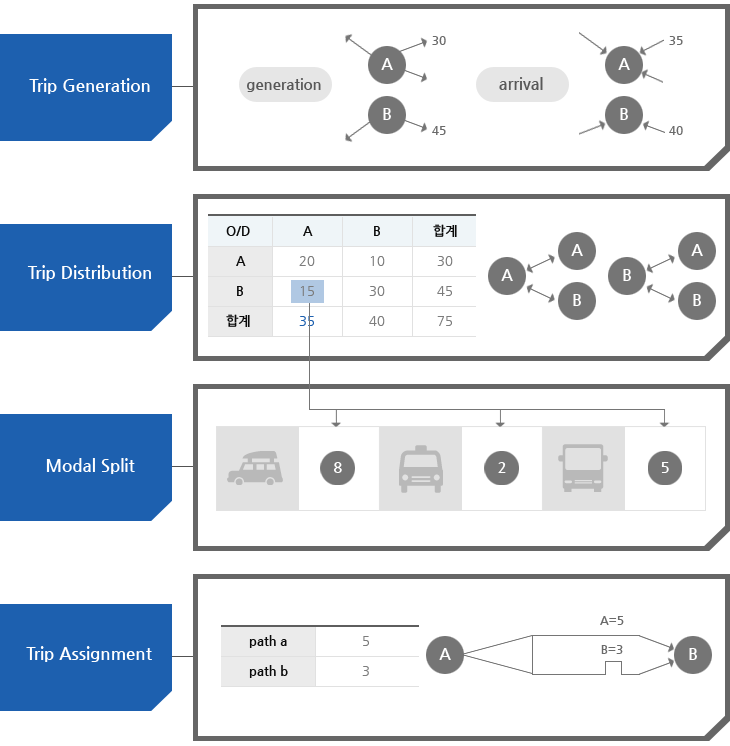
- The four steps of this model are trip generation -> trip distribution -> mode choice -> trip assignment
- Trip generation: estimate trip production and trip attraction of transport zone by using socioeconomic indexes.
- Trip distribution: build cross-travel volume between transport zones by distributing trip generation and arrival.
- Mode choice: subdivide cross-travel volume between transport zones for each mode of transport that users can choose.
- Trip assignment: generate reasonable paths between transport zones and assign travel volume of each mode of transport to those paths.
[Four-step transport demand forecast process]
Integrated model
- The integrated model predicts transport demand by integrating all or some of the four-step demand forecast process.
- Different integrated models include trip generation-mode share, trip distribution-mode share, trip distribution-trip assignment, and direct demand
Activity-based model
- This model was recently tried out in order to overcome the limits of travel-based four-step models.
- Analyzes actives and trips derived from activities of individuals or households for each time period, mode of transport, transport networks, and other conditions.
- It takes great amount of data and time to build this model. The exact methodology of building the model has not yet been proposed.
- Many types of models (single activity, Portland, activity condition, regulation-based, active population in specific time and space) are being developed.
Reference
- Jeonghyun RHO, 1999, Transport Plan, Nanam Publishing House.
- Yongtaek LIM, Seunggeol Baek, Jingi Eom, Hyunmyeong Kim, Jun Lee, Jingyeong Park, 2013, Transport Plan, Cheong Moon Gak Publisher.
- Daesik YUN, 2010, Transport Demand Analysis, Pakyoungsa.
- Jemu WON, 2010, Easy Urban Transport, Pakyoungsa.
- Gangwon LIM, 1997, Urban Transport Plan, Seoul University Press.